Request Scene Model (RSM)
What is the request scene model
The request scenario model is based on the perspective of the client. It describes the abstract model of the client from triggering the request intent to receiving the request result. It consists of four stages: request timing, request behavior, request event, and response management. For example, when making a request, you often need to think about the following questions,
- When the request is made;
- Whether to display the request status;
- Do you need to retry the request on failure;
- How to process the response data;
- Do you need to encrypt the request parameters;
- Whether to cache the frequently used response data;
- How to operate data across pages;
- How to process requests in a weak or disconnected network environment;
- ...
fetch or axios are often more focused on how to interact with the server, but we always need to deal with the above problems by ourselves. These functions that are beneficial to application performance and stability will always allow programmers to write low-maintenance sexual code. The request scene model is to abstract all links from preparing the request to processing the response data, so as to cover the model of the entire CS interaction life cycle from the perspective of the front end. alova is a library that requests scene models, it is a supplement to request libraries such as axios, not a substitute.
CS interaction: generally refers to data interaction between all client types and servers
Request scene model
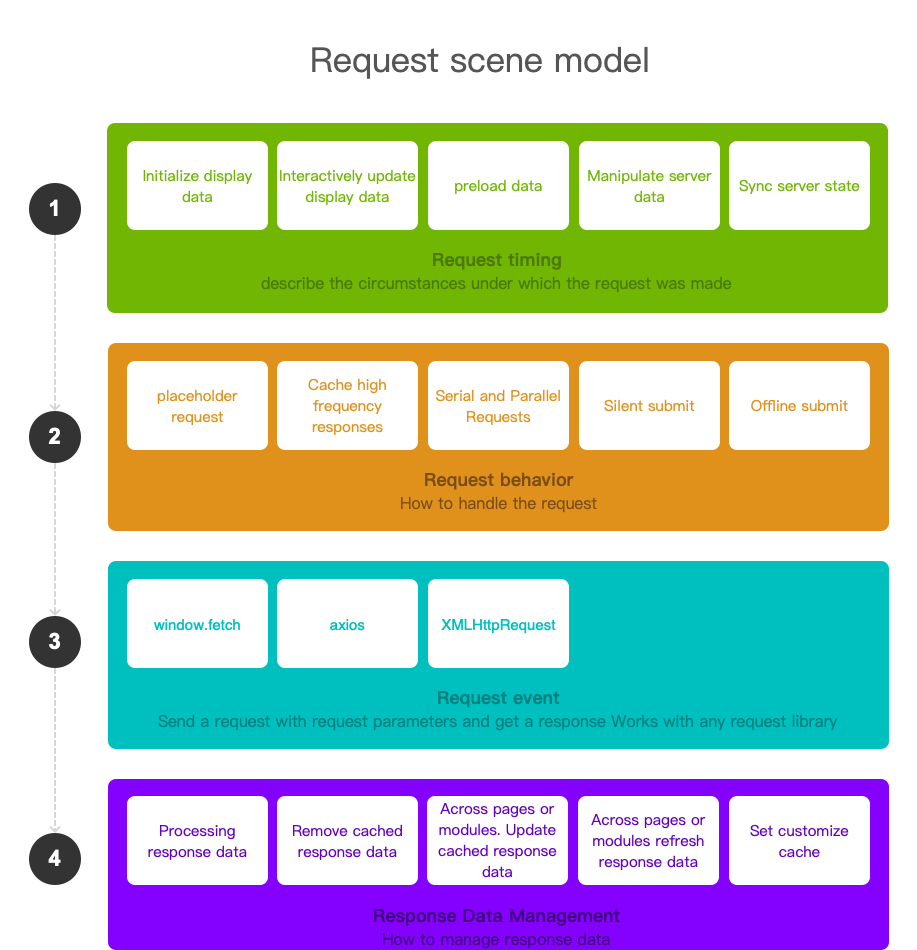
request timing
Describe when a request needs to be made, implemented with useHook in alova.
- Initialize display data, such as just entering a certain interface or sub-interface;
- Human-computer interaction triggers CS interaction, and the request needs to be changed again, such as page turning, filtering, sorting, fuzzy search, etc.;
- Send requests in an anti-shake manner, avoid view data flickering, and reduce server pressure
- Preloading data, such as preloading the content of the next page in a page, predicting that the user clicks a button to pre-fetch data;
- To operate server data, it is necessary to issue a request for addition, deletion, modification and query, such as submitting data, deleting data, etc.;
- Synchronize server status, such as polling requests in scenarios where data changes rapidly, and re-pull data after operating a certain data;
Request Behavior
Describes how to process the request, implemented as a Method abstraction in alova.
- Placeholder request, when requesting, display loading, skeleton diagram, or real data used last time;
- Cache high-frequency responses, multiple execution requests will use fresh data;
- Multi-request serial and parallel;
- The retry mechanism of important interfaces reduces the probability of request failure caused by network instability;
- Submit silently. When you only care about submitting data, directly respond to the success event after submitting the request, and the background guarantees that the request is successful;
- Offline submission, the submitted data will be temporarily stored locally when offline, and then submitted after the network connection;
request event
Indicates sending a request with request parameters and getting a response. alova can work with any request library or native solution such as axios, fetch, XMLHttpRequest.
Response management
alova makes the response data stateful and manages it in a unified manner, refreshes the view data and operates the cache at the request level, avoids operations at the component level, and is more elegant and unified.
- Remove the cached response data, which will be pulled from the server when the request is made again;
- Update the cached response data, which can update the response data at any location, which is very helpful for updating data across pages;
- Refresh the response data, which can re-refresh the response data at any position, and is also very helpful for updating data across pages;
- Customize the cache setting. When requesting batch data, you can manually set the cache for the batch data one by one, so as to meet the cache hit of subsequent single data;
 Is using alova in your project? please tell me!
Is using alova in your project? please tell me!